Energy Insider: State Grid Spends Big to Tackle Transmission Bottleneck, Solar Firms Struggle Amid Overcapacity
Listen to the full version

In this week’s Caixin energy wrap, we analyze China’s biggest climate and energy news on policy, industry, projects and more:
●State Grid spends big to tackle transmission bottleneck
●Solar manufacturers face mounting losses
●Renewable power capacity keeps growing
●Shanghai plans big for offshore wind power
●Long-term green power contracts on the horizon
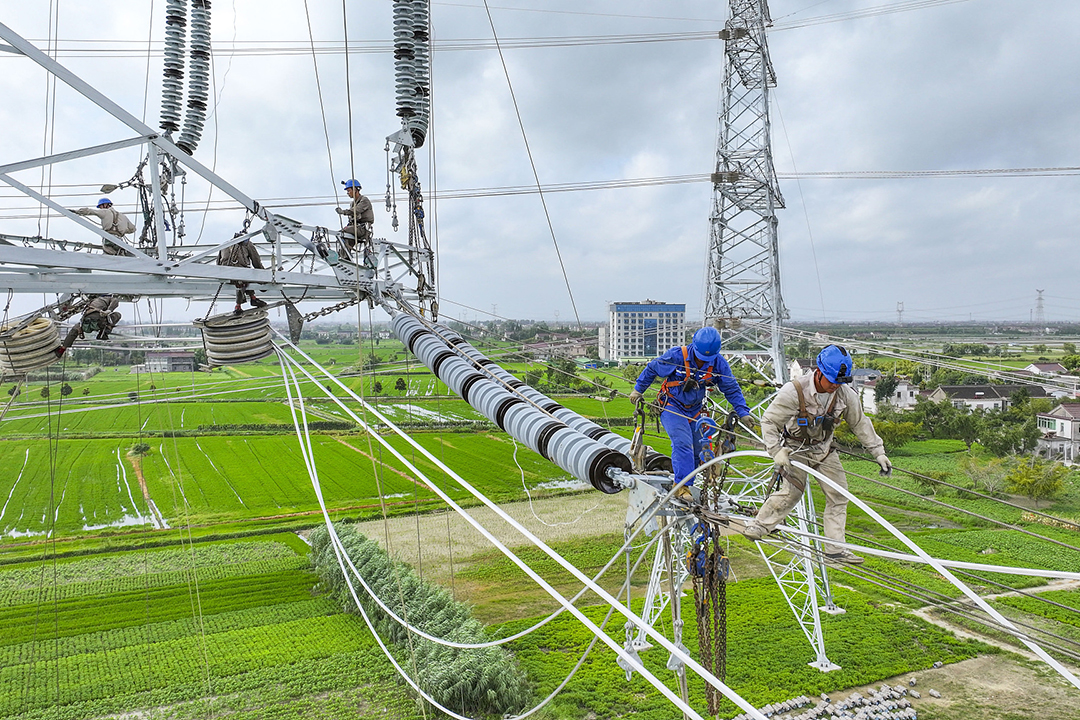
In focus: State Grid increases investment for transmission infrastructure
Download our app to receive breaking news alerts and read the news on the go.
Get our weekly free Must-Read newsletter.
- DIGEST HUB
- State Grid of China plans to invest 600 billion yuan ($83 billion) by the end of this year to improve transmission infrastructure and tackle bottlenecks.
- Many Chinese solar manufacturers face losses due to overcapacity and price wars, urging industry consolidation.
- China installed 134 GW of renewable power in the first half of 2024, with a 24% year-on-year increase, and Shanghai plans 29.3 GW of offshore wind projects to enhance energy security.
## Summary
This week's Caixin energy wrap outlines key developments in China's climate and energy sector, focusing on policy, industry trends, and significant projects [para. 1].
### State Grid's Increased Investment in Transmission Infrastructure
**What's New**: The State Grid Corp. of China has significantly ramped up spending to address transmission bottlenecks. The aim is to facilitate the transfer of wind and solar power from western regions to industrial hubs in the east. This year, the State Grid is set to invest a record 600 billion yuan ($83 billion), an increase of 71.1 billion yuan from 2023, to improve the power system, rural grid connections, and network digitalization [para. 6].
**Why It Matters**: China recently marked a landmark moment as its installed wind and solar power capacity exceeded its coal power capacity for the first time. However, inadequate long-distance transmission infrastructure poses major challenges for continued renewable energy development [para. 8].
### Solar Manufacturers Facing Overcapacity and Price Wars
**What's New**: Overcapacity and a resulting price war have forced many Chinese solar manufacturers to slow down or halt their production. Industry consolidation is being urged to combat the financial strain, as many companies posted losses for the first half of the year. Notably, the Communist Party's top decision-making body has advised industries to practice self-discipline and curb excessive competition [para. 9][para. 11].
**Why It Matters**: Severe overcapacity has driven the price of solar panels below production cost, plunging to around 0.8 yuan per watt in July from nearly 2 yuan in early January last year. This financial strain necessitates faster industry consolidation to maintain viability [para. 12].
### Renewable Power Capacity Growth
**What's New**: China installed 134 gigawatts (GW) of renewable power capacity in the first half of 2024, reflecting a 24% year-on-year increase. This includes wind, solar, hydro, and biomass power, with solar power leading the growth by adding 102 GW. Renewable sources now account for nearly 54% of China’s cumulative power capacity [para. 13].
**Why It Matters**: The rapid growth in renewable capacities, particularly in wind and solar energy, positions China to meet new electricity demand and potentially peak its carbon emissions before 2025, as emphasized by a Greenpeace East Asia project lead [para. 15].
### Shanghai's Offshore Wind Power Ambitions
**What's New**: Shanghai plans to build 29.3 GW of offshore wind power plants, which would account for nearly 80% of China's current offshore wind capacity. These plants are expected to generate 100 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity annually, more than half of Shanghai’s consumption in 2023 [para. 16].
**Why It Matters**: By leveraging offshore wind resources, Shanghai aims to enhance its energy security, reducing dependency on imported electricity. Other coastal regions in China are also rapidly advancing offshore wind power projects [para. 18].
### Long-Term Green Power Contracts
**What's New**: The Beijing Power Exchange Center is contemplating the introduction of long-term contracts for green electricity trading. These contracts would typically last five years or more, compared to the current one-year agreements [para. 20].
**Why It Matters**: Increasing green electricity trading aligns with China’s broader goals for renewable energy usage. Long-term contracts would provide stability for both suppliers and consumers, ensuring reliable supply and income while mitigating price volatility [para. 21].
The summarized content encapsulates the major developments in China’s energy landscape, highlighting the country's robust steps toward addressing infrastructure challenges, industry consolidation, and leveraging renewable resources for sustainable growth.
- State Grid Corporation of China
- The State Grid Corporation of China has ramped up investment in ultra-high-voltage transmission infrastructure to alleviate transmission bottlenecks, aiming to connect wind and solar power from western regions to the eastern economic hubs. By the end of this year, they will have invested a record 600 billion yuan ($83 billion), enhancing the power system, integrating rural grids, and digitalizing the network. This initiative is crucial for advancing China's renewable energy development.
- By the end of June 2024:
- Nearly 54% of China’s cumulative power capacity came from renewable sources.
- 2024-07-25:
- Wang Bohua, honorary chairman of the China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA), reported at a solar conference in Zhejiang that many Chinese solar manufacturers slowed or halted production in the first half of the year.
- 2024-07-25:
- A CPIA report was released, stating that the opening bid price for solar panels had fallen to about 0.8 yuan in July 2024.
- 2024-07-26:
- Xinhua News Agency reported that the State Grid Corp. of China has been increasing its spending on building ultra-high-voltage transmission lines this year.
- 2024-07-30:
- The Communist Party's top decision-making body urged industries to enhance self-discipline and avoid fierce domestic competition.
- 2024-07-31:
- An official from the National Energy Administration (NEA) announced that China installed 134 gigawatts (GW) of renewable power capacity in the first half of 2024.
- PODCAST
- MOST POPULAR







 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google
 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with 财新
Sign in with 财新